💻Arduino Programming💻
💻Arduino Programming💻
Introduction to Arduino (8/11/21)
In this lesson, we are introduced to Arduino Programming and given a series of introductory activities and challenges to test our understanding of Arduino programming.
Activity 1
For our very first activity, we were tasked to make a code to control the lights on the Arduino board "blink".
To do this activity, I did the following steps:
Step 1: Launch the Arduino programming software
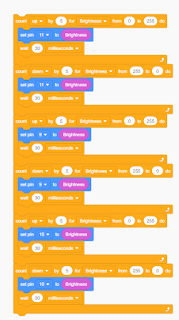
// initialize digital pin 5 as an output.
pinMode(5, OUTPUT);
}
// the loop function runs over and over again forever
void loop() {
digitalWrite(5, HIGH); // turn the LED on (HIGH is the voltage level)
delay(5000); // wait for 5 second
digitalWrite(5, LOW); // turn the LED off by making the voltage LOW
delay(3000); // wait for 3 second
}
Video Link: https://youtu.be/y8RNvsiy3TM
Activity 2:
In our second activity, we were tasked to program the Arduino board such that we could control the lights on the Arduino board with a button also located on the Arduino board.
To perform this activities, here are the steps I did:
Step 1: Launch the Arduino programming software
Step 2: Under the file tab, click onto Example-> Digital->DigitalInputPullup and the code should be seen
void setup()
{
//start
serial connection
Serial.begin(9600);
//configure
pin 2 as an input and enable the internal pull-up resistor
pinMode(2,
INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(13,
OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
//read the
pushbutton value into a variable
int sensorVal = digitalRead(2);
//print out
the value of the pushbutton
Serial.println(sensorVal);
// Keep in
mind the pull-up means the pushbutton's logic is inverted. It goes
// HIGH when
it's open, and LOW when it's pressed. Turn on pin 13 when the
// button's
pressed, and off when it's not:
if
(sensorVal == HIGH) {
digitalWrite(13,
LOW);
} else {
for
(int i=0; i < 5; i++)
{
//ON PIN13
FOR 5 MS AND OFF FOR 5MS
digitalWrite(13,
HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(13,
LOW);
delay(500);
}
#include
"pitches.h"
// notes in
the melody:
int melody[]
= {
NOTE_C4, NOTE_G3, NOTE_G3, NOTE_A3, NOTE_G3, 0, NOTE_B3, NOTE_C4
};
// note
durations: 4 = quarter note, 8 = eighth note, etc.:
int noteDurations[]
= {
4, 8,
8, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4
};
void setup()
{
//start serial connection
Serial.begin(9600);
//configure pin 2 as an input and enable the internal pull-up resistor
pinMode(2,
INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(13,
OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
//read the pushbutton value into a variable
int sensorVal = digitalRead(2);
//print out the value of the pushbutton
Serial.println(sensorVal);
//
Keep in mind the pull-up means the pushbutton's logic is inverted. It
goes
//
HIGH when it's open, and LOW when it's pressed. Turn on pin 13 when the
//
button's pressed, and off when it's not:
if
(sensorVal == HIGH) {
digitalWrite(13,
LOW);
noTone(8);
//DO NOTHING!
}
else {
digitalWrite(13,
HIGH);
//PLAY TONE!
}
//
iterate over the notes of the melody:
for (int thisNote =
0; thisNote < 8; thisNote++) {
// to calculate the note duration, take one second divided by the note
type.
//e.g. quarter note = 1000 / 4, eighth note = 1000/8, etc.
int noteDuration = 1000 / noteDurations[thisNote];
tone(8,
melody[thisNote], noteDuration);
// to distinguish the notes, set a minimum time between them.
// the note's duration + 30% seems to work well:
int pauseBetweenNotes = noteDuration * 1.30;
delay(pauseBetweenNotes);
// stop the tone playing:
noTone(8);
}
Step 3: Click on the Upload button at the top and the program will be uploaded onto the Arduino board.
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a
servo
// twelve servo objects can be created on most boards
int pos = 0; // variable
to store the servo position
void setup() {
myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin
9 to the servo object
}
void loop() {
for (pos = 20; pos <=
150; pos += 1) { // goes from 0 degrees to 180 degrees
// in steps of 1 degree
myservo.write(pos);
// tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(3000);
// waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position
}
for (pos = 150; pos >=
20; pos -= 1) { // goes from 180 degrees to 0 degrees
myservo.write(pos);
// tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(3000);
// waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position
}
for (pos = 20; pos >=
150; pos -= 1) { // goes from 180 degrees to 0 degrees
myservo.write(pos);
// tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(15);
// waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position

















Comments
Post a Comment